sandbox/alimare/1_test_cases/reinit_LS.c
LS_reinit() test case
// still a bug with the extract_root_x => divergence.
This case is extracted from Russo et al.,1999 we initialize a perturbed distance field, where the zero level-set is an ellipse of the form: \displaystyle \phi (x,y,0) = f(x,y) \times g(x,y) where the perturbation is : \displaystyle f(x,y) = \epsilon + (x - x_0)^2 +(y - y_0)^2 and the ellipse is : \displaystyle g(x,y) = \left( \sqrt{\frac{x^2}{A^2}+\frac{y^2}{B^2}} -R \right) with A=2, B=1, R = 1 , x_0 = 3.5, y_0 = 2..
We want to recover a perfect distance field, remove the initial perturbation.
#define BICUBIC 1
#define BGHOSTS 2
#include "popinet/distance_point_ellipse.h"
#include "alimare/alex_functions.h"
#include "alimare/LS_reinit.h"
#include "alimare/basic_geom.h"
#include "view.h"
double perturb (double x, double y, double eps, coord center){
return eps + sq(x - center.x) + sq(y - center.y);
}
void draw_isolines(scalar s, double smin, double smax, int niso, int w){
vertex scalar vdist[];
cell2node(s,vdist);
boundary ({vdist});
for (double sval = smin ; sval <= smax; sval += (smax-smin)/niso){
isoline ("vdist", sval, lw = w);
}
}
#define Pi 3.141592653589793
norm mynorm(scalar f, scalar f2, double threshold){For this test case, we use a special norm defined by the author, which ignores the points below a specific threshold, f > \text{threshold}
double avg = 0., rms = 0., max = 0., volume = 0.;
foreach(reduction(max:max) reduction(+:avg)
reduction(+:rms) reduction(+:volume))
if (f[] != nodata && dv() > 0. && f2[] > threshold) {
double v = fabs(f[]);
if (v > max) max = v;
volume += dv();
avg += dv()*v;
rms += dv()*sq(v);
}
norm n;
n.avg = volume ? avg/volume : 0.;
n.rms = volume ? sqrt(rms/volume) : 0.;
n.max = max;
n.volume = volume;
return n;
}
norm mynorm2(scalar f, scalar f2, double threshold){This second norm selects points such that |f| < \text{threshold}.
double avg = 0., rms = 0., max = 0., volume = 0.;
foreach(reduction(max:max) reduction(+:avg)
reduction(+:rms) reduction(+:volume))
if (f[] != nodata && dv() > 0. && fabs(f2[]) < threshold) {
double v = fabs(f[]);
if (v > max) max = v;
volume += dv();
avg += dv()*v;
rms += dv()*sq(v);
}
norm n;
n.avg = volume ? avg/volume : 0.;
n.rms = volume ? sqrt(rms/volume) : 0.;
n.max = max;
n.volume = volume;
return n;
}
scalar dist[];
scalar * level_set = {dist};
int main() {
origin (-5., -5.);
L0 = 10;
int MAXLEVEL = 6;
for(MAXLEVEL = 6; MAXLEVEL < 9; MAXLEVEL++){
init_grid (1 << MAXLEVEL);
double A = 4., B=2.;
coord center_perturb = {3.5,2.};
foreach(){
double a,b;
// dist[] = DistancePointEllipse(A,B,x,y,&a, &b);
dist[] = DistancePointEllipse(A,B,x,y,&a, &b)*
perturb(x,y, 0.1, center_perturb);
}
boundary({dist});
squares ("dist", map = cool_warm, min = -2, max = 2);
draw_isolines(dist, -2., 2., 20, 1);
save("dist_init.png");
int nbit = LS_reinit(dist, it_max = 1 << (MAXLEVEL+1));
squares ("dist", map = cool_warm, min = -2, max = 2);
draw_isolines(dist, -2., 2., 20, 1);
save("dist_first_reinit.png");
scalar err[],LogErr[];
foreach(){
double a,b;
err[] = dist[] - DistancePointEllipse(A,B,x,y,&a, &b);
LogErr[] = log(fabs(err[])+1.e-16);
}
boundary({err,LogErr});
norm n = mynorm(err,dist,-0.8);
norm n2 = mynorm2(err,dist,1.2*L0/(1 << grid->maxdepth));
fprintf(stderr, "%d %g %g %g %g %g %g %d\n",1<<MAXLEVEL, n.avg, n.rms,n.max,
n2.avg, n2.rms,n2.max, nbit);
if(MAXLEVEL == 8){
squares ("LogErr", min = log(n.max)-6, max = log(n.max));
save("err.png");
}
}
exit(1);
}We show here the initial and final level-set for the same isovalues.
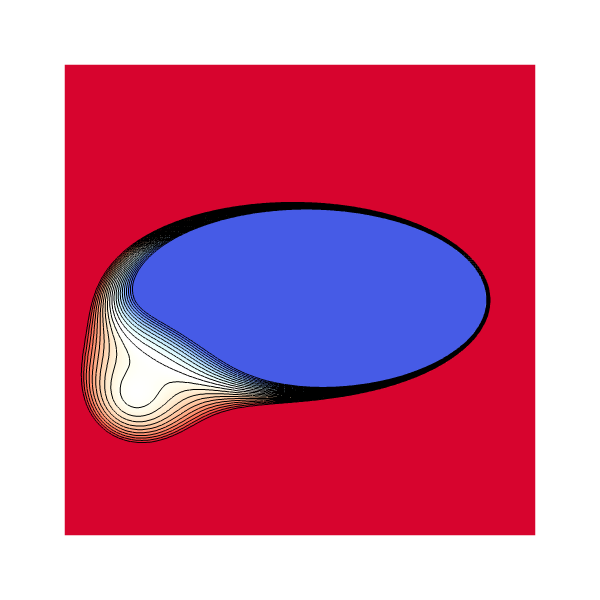
Initial level-set
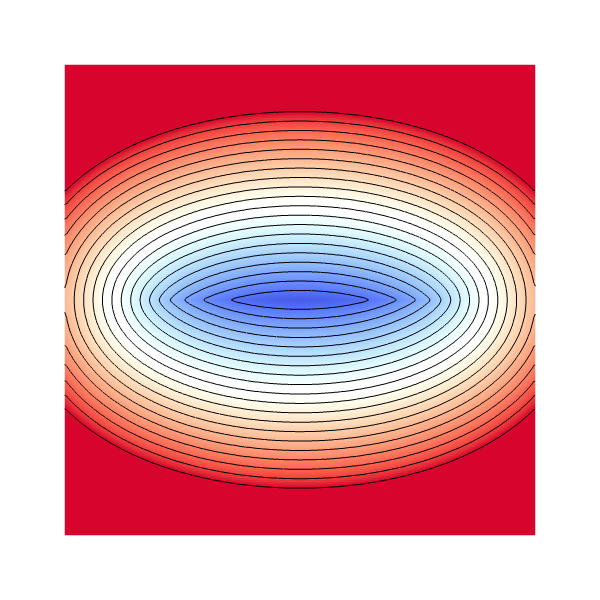
First reinit
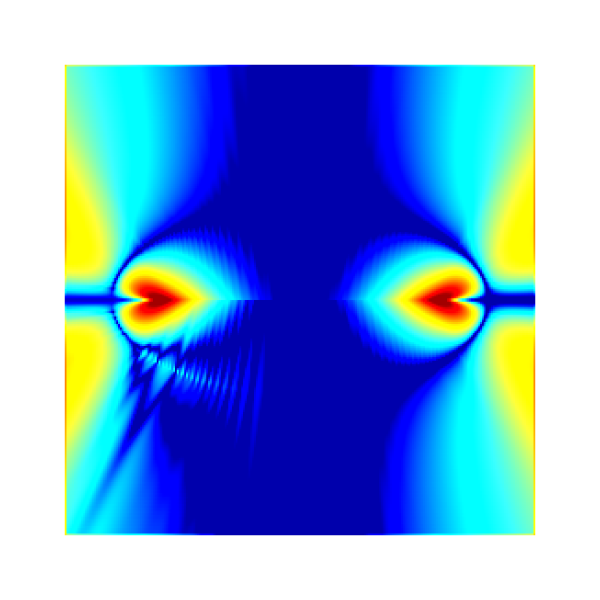
Error, logscale between 10^{-4} and 10^{-1}
f(x) = a + b*x
f1(x) = a1 + b1*x
f2(x) = a2 + b2*x
fit f(x) 'log' u (log($1)):(log($2)) via a,b
fit f1(x) 'log' u (log($1)):(log($3)) via a1,b1
fit f2(x) 'log' u (log($1)):(log($4)) via a2,b2
ftitle(a,b) = sprintf("%.2f-%4.2f x", a, -b)
set logscale xy
set xrange [32:512]
set xtics 32,2,512
set format y "%.1e"
plot 'log' u 1:2 t 'avg', exp(f(log(x))) t ftitle(a,b), \
'log' u 1:3 t 'rms', exp(f1(log(x))) t ftitle(a1,b1), \
'log' u 1:4 t 'max', exp(f2(log(x))) t ftitle(a2,b2)error analysis (script)
f(x) = a + b*x
f1(x) = a1 + b1*x
f2(x) = a2 + b2*x
unset logscale
unset xrange
fit f(x) 'log' u (log($1)):(log($5)) via a,b
fit f1(x) 'log' u (log($1)):(log($6)) via a1,b1
fit f2(x) 'log' u (log($1)):(log($7)) via a2,b2
ftitle(a,b) = sprintf("%.2f-%4.2f x", a, -b)
set logscale xy
set xrange [32:512]
set xtics 32,2,512
set format y "%.1e"
plot 'log' u 1:5 t 'avg', exp(f(log(x))) t ftitle(a,b), \
'log' u 1:6 t 'rms', exp(f1(log(x))) t ftitle(a1,b1), \
'log' u 1:7 t 'max', exp(f2(log(x))) t ftitle(a2,b2)error analysis 0-level-set (script)
Here we study the value of the level-set function on a set of points where it is theoretically 0, we show that we have also a 3^{rd} convergence.
References
| [russo_remark_2000] |
Giovanni Russo and Peter Smereka. A remark on computing distance functions. Journal of Computational Physics, 163(1):51–67, 2000. |

